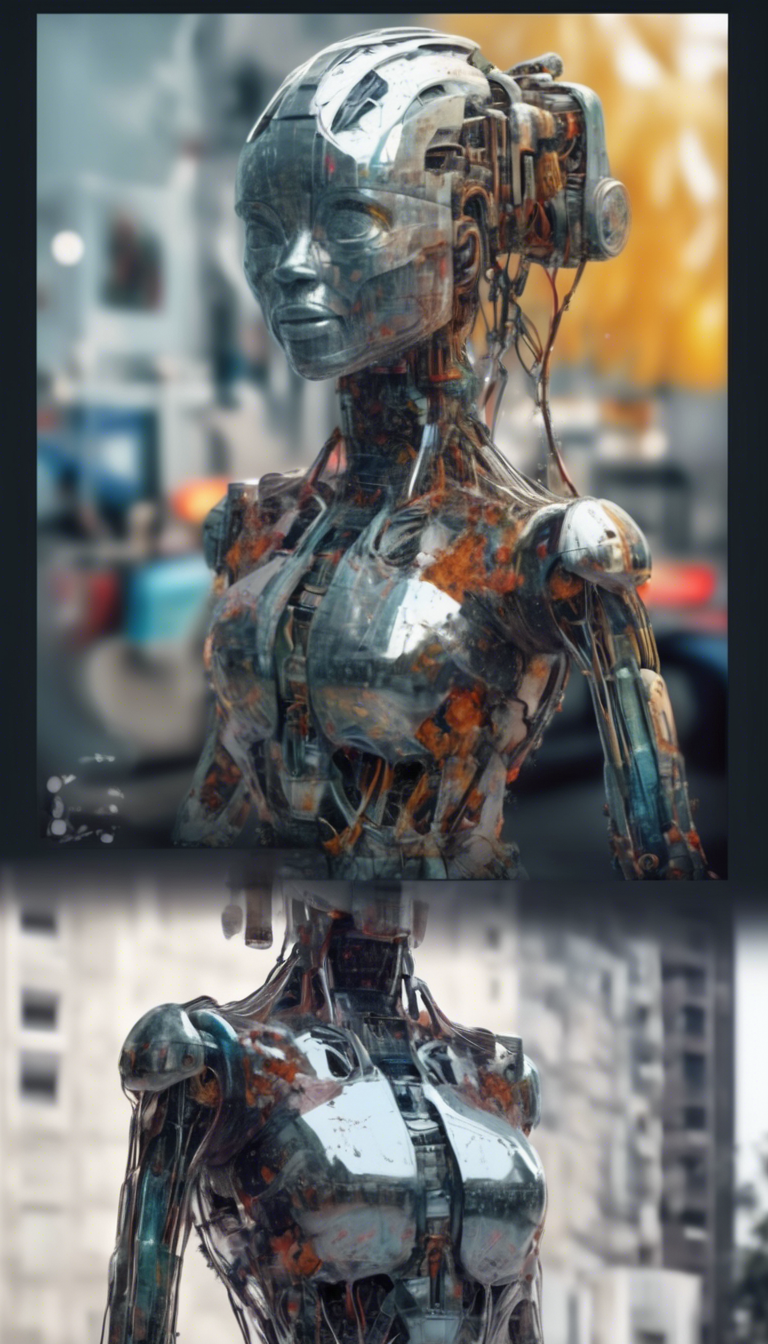
The Debate on Whether AI Images Can Be Considered Art
The rise of artificial intelligence in creative fields has sparked intense debate about whether AI-generated images can truly be classified as art. Advocates argue that AI has opened the floodgates to new forms of self-expression, while detractors insist that these images lack the human touch that defines genuine artistic endeavor. As we delve into this topic, it’s essential to evaluate the components that characterize art and the unique aspects of AI-generated imagery.
At the heart of this discussion lies the definition of art itself. Traditionally, art has been viewed as a human-centered activity, rooted in emotion, intention, and creativity. Artists pour their thoughts, feelings, and experiences into their work. This emotional investment often helps viewers connect with the piece on a deeper level. In contrast, AI can analyze patterns, styles, and techniques from vast datasets, producing images based on algorithms rather than personal expression. As a result, many argue that AI images are not art because they lack the essential human experience and emotion.
Moreover, the process of creating art typically requires a certain level of skill and personal touch. Artists painstakingly develop their craft over years, honing their techniques and unique styles. In contrast, AI relies on pre-existing data to generate images, often resulting in outputs that mirror existing styles without any original thought. This mechanistic approach raises the question: can art be created without the artist’s individual perspective? Critics heavily emphasize this point, believing that without a personal connection, AI images cannot fulfill the criteria needed to be deemed art.
Additionally, many consider intention as a key factor in the definition of art. Artists usually create with specific goals or messages in mind, whether it be societal commentary, personal exploration, or even pure aesthetics. On the other hand, AI doesn’t possess intentions or desires. It doesn’t “want” to express something; it operates based on data input and outputs based on pre-established algorithms. This absence of intention and emotional context furthers the argument that AI images might not qualify as art.
On the flip side, one could argue that the outcome of AI image generation can indeed convey meaning. For example, the juxtaposition of different styles and themes in AI-generated pieces can evoke emotions or provoke thought among viewers. This suggests that even without human intention, AI images can stimulate connections and awareness, displaying qualities traditionally associated with art. Moreover, some artists are beginning to utilize AI as a tool, blending their creativity with technology. This collaboration blurs the lines between traditional and digital art forms, expanding the notion of what can be considered art in the modern age.
It’s also worth noting that the technology behind AI-generated imagery is advancing at a rapid pace. As AI systems become more sophisticated, they might mimic the nuances of artistic expression and technique more closely. This raises an interesting question: if machines can replicate the subtleties of human creativity, does it not open new avenues for defining art? Could it lead us to a broader interpretation where AI images are included in the artistic dialogue?
However, despite its potential, many still believe the core issue remains unanswered. Here are some points to consider:
- Expression: Does the resulting imagery evoke emotion in a way that traditional art does?
- Skill: Can AI truly demonstrate the mastery of technique that comes with human experience?
- Intent: Without the drive to communicate a message, can AI images genuinely be art?
- Impact: How do audiences perceive AI-generated images in the context of the artistic value?
- Cultural Relevance: Does the art community accept AI art as part of the contemporary art landscape?
The debate around whether AI images can be classified as art is complex and multifaceted. It raises fundamental questions about creativity, emotion, and the human experience. Regardless of where you stand on the issue, it’s clear that we are witnessing a significant evolution in the realm of art. As technology progresses, so too will our perceptions of what constitutes art, potentially reshaping the landscape of creativity for generations to come. Ultimately, the discussion will continue, challenging definitions and pushing boundaries in exciting new directions.
Exploring the Emotional Connection to Traditional Art versus AI-Generated Images
Art has always been a reflection of human emotion, experience, and culture. Traditional art forms, whether it’s painting, sculpture, or photography, often embody the artist’s unique perspective and emotional depth. This emotional connection is something many find hard to replicate in AI-generated images. While technology plays a significant role in today’s artistic expression, the essence of emotion in art comes under scrutiny when comparing traditional works to their AI counterparts.
Traditional art invites viewers into the artist’s world. Each brushstroke, color choice, and material used tells a story, often rooted in the creator’s personal experiences. When you look at a classic painting, you can’t help but feel a connection to the artist. You may wonder what emotions spurred the creation, the challenges faced, or the cultural backdrop that influenced the piece. These thoughts evoke empathy, curiosity, and admiration. In contrast, AI-generated images are typically created through algorithms and input data. They lack the personal experiences and emotional investment that human artists pour into their creations.
One of the key differences lies in the element of intention. Traditional artists create not just to produce an image but to convey a message, provoke thought, or evoke emotion. For instance:
- Painting: An artist may capture the struggles of society through dark hues and distorted forms, illustrating the despair they perceive.
- Sculpture: A sculpture might represent freedom with open arms, carved from stone as a testament to the effort and thought put into its creation.
- Photography: A poignant photograph can depict raw, unfiltered emotion, capturing a fleeting moment that resonates deeply with the viewer.
On the other hand, AI-generated images often stem from technical parameters devoid of human nuance. They are created using pre-existing patterns and styles, reshaped by algorithms to produce something aesthetically pleasing. However, this process raises questions about authenticity. Can an image generated by lines of code truly evoke the same emotions as one crafted by a human hand? Many argue it cannot. While these images may be visually stunning, the absence of an underlying emotional journey stifles their potential impact.
Consider the role of imperfection in traditional art. Artists often embrace flaws as part of their expressive toolkit. These imperfections make a piece unique—reflecting the human experience of error, growth, and evolution. In contrast, AI-generated images tend to be polished and precise, often leading to an almost sterile outcome. The human touch, with all its irregularities and unpredictability, is what often makes traditional art resonate profoundly with viewers.
Community plays a vital role in fostering an emotional connection to art. Traditional artists often engage with their communities, drawing inspiration from shared experiences, cultural heritage, and collective emotions. Exhibitions, local galleries, and art fairs provide opportunities for dialogue, where viewers can connect with artists and other admirers. This interaction enhances the emotional experience of viewing art; you’re part of a shared moment, an experience that transcends the visual. In contrast, AI-generated images primarily exist in isolation, often circulating online without a community connection. This lack of reciprocal experience diminishes their emotional weight.
While AI technology continues to advance, it opens up avenues for creativity that were previously unimaginable. Yet, it is crucial to understand the limits of what AI can offer. Can it replicate the emotional depth found in human-centric art? Many would argue it falls short. Critics of AI-generated images emphasize the importance of human experience, advocating for the uniqueness of traditional art and its irreplaceable emotional bond.
As art continues to evolve, society must grapple with these distinctions. The emotional connections forged through traditional art remind us that art’s value extends beyond aesthetics. It symbolizes the shared human experience, revealing our struggles, triumphs, and dreams. AI-generated images may complement the art landscape, but they are unlikely to replace the irreplaceable human touch that gives traditional art its powerful emotional resonance.
Ultimately, the conversation surrounding AI and art is a reflection of our broader relationship with technology. As we navigate this complex interplay, one thing remains clear: the heart and soul embedded in traditional art are irreplaceable.
Conclusion
The discussion surrounding the notion that "AI images are not art" invites us to reflect deeply on what constitutes art in our ever-evolving cultural landscape. At the heart of this debate lies a fundamental question of intent, creativity, and emotional resonance. When we consider traditional art, we often envision the artist pouring their emotions, thoughts, and experiences into a canvas or a sculpture. This intimate act of creation sparks an emotional connection between the artist and the viewer, one that transcends the physicality of the artwork itself.
AI-generated images, while undeniably impressive in their visual appeal and technical execution, often lack this intrinsic emotional layer. Algorithms are engineered to mimic existing styles and compositions, drawing upon vast datasets of art history and current trends. They can produce striking images that capture moments or concepts, but they do so devoid of a personal journey. The artist’s intention—a key element in defining art—remains absent in the creation of AI images. This absence leads many to argue that these creations, while visually enticing, fundamentally differ from traditional artwork in terms of emotional engagement.
Emotional connection plays a pivotal role in the definition of art. People often find themselves moved by an artist’s human experience portrayed in their work. A painting by Van Gogh or a sculpture by Michelangelo carries narratives of struggle, triumph, and a tactile human experience. Viewers can connect with the artist on a personal level, perceiving their emotions through strokes of paint and chisels of stone. On the contrary, AI-generated images do not convey a story rooted in human existence. They may evoke feelings—a beautiful landscape might stir a sense of wonder, while a digitally manipulated portrait might provoke introspection. However, these feelings arise from the viewer’s experience rather than the creator’s narrative.
The debate does not simply center on whether AI can create visuals but delves into the philosophical realms of creativity itself. Can creativity exist without consciousness? Traditional artists draw from deep wells of inspiration, aligning their work with cultural, social, and personal contexts. Their artworks reflect their viewpoints and life experiences. In contrast, AI operates based on programming, lacking the consciousness to imbue its creations with personal significance. Thus, while it might produce aesthetically compelling images, there remains a consensus among many art enthusiasts and critics about the lack of artwork’s depth in AI-generated visuals.
Moreover, this digital age prompts us to rethink the very essence of creativity. Some argue that the collaborative potential between human artists and AI could lead to innovative forms of expression. However, even in such collaborations, it’s important to acknowledge who holds the creative reins. Is it the human guiding the AI, or does the AI become a co-creator? This poses a challenge to the traditional understanding of ownership and authorship in art.
As we navigate the impacts of technology on creativity, we must also consider the art communities and industries shaped by these advancements. Many creatives feel concerned about the rise of AI-generated art displacing traditional artists. The implications extend beyond aesthetics; they affect creative livelihood and the sustainability of artistry as a vocation. As AI becomes more prevalent in design, illustration, and visual storytelling, there’s a palpable fear of diminishing demand for human-crafted work. Ensuring a supportive ecosystem for both traditional artists and emerging AI technologies is critical in preserving the rich tapestry of creative expression.
As the debate around whether "AI images are not art" continues, it’s clear that our perceptions of art are in flux. While AI can generate impressive visuals and contribute to artistic conversations, it often fails to connect with viewers on an emotional level like traditional art does. In appreciating art, the stories, intentions, and emotions captured within an artwork remain irreplaceable. Perhaps we must embrace a nuanced understanding of creativity, one where AI serves as a tool to enhance human artistry rather than replace it. This balance could nurture an ongoing dialogue about creativity, allowing us to celebrate the diverse methodologies that define the ever-evolving nature of art.